Digital transformation and innovation performance
By sorting out the previous research results, it can be found that the study on the relationship between digital transformation and innovation performance mainly starts from different perspectives of enterprise innovation. It mainly involves enterprise model innovation, enterprise green innovation, enterprise regional innovation, enterprise mechanism innovation and other aspects.
In essence, enterprise innovation is the performance of the whole staff inside the enterprise. By introducing digital leadership into the process of enterprise digital transformation, and taking digital enterprise platform as an intermediary factor, this paper studies the relationship between digital leadership and enterprise innovation performance. Found digital leadership through the digital platform to improve the innovation performance of enterprises, mainly for the digital platform for leadership and digital ability positively correlated relationship, then platform digital capability and innovation performance were positively correlated relationship3. Therefore, digital leadership can promote the innovation performance of enterprises.
Innovation in general can be regarded as the integration of various knowledge accumulation. Enterprise innovation is a complex dynamic process. Enterprise open innovation is divided into two dimensions of innovation opening depth and innovation opening breadth4. Using the dynamic capability theory, we find that in the digital context, the depth of innovation and openness can significantly improve the growth performance of new ventures. Moreover, business model innovation plays an intermediary role between the two, while the breadth of innovation openness has little impact on new ventures. Further research finds that enterprises can promote enterprise innovation through mechanisms such as realizing open network innovation, leading to organizational management innovation and improving the level of enterprise human capital5. Comprehensive digital transformation can promote innovation more effectively than just applying digital technology.
As enterprise innovation is affected by environmental restrictions and regional differences, the degree of influence of digital transformation on enterprise innovation performance is slightly different. Innovation activity has uncertainty in the process and fuzziness in the result. In order to avoid the risk of future innovation returns, from the perspective of cross-regional innovation, parallel trend, placebo test, replacement index and instrumental variable method are adopted to conduct a stability test on whether digital transformation can significantly improve the independent innovation level of remote subsidiaries and promote the cross-regional development of enterprises. It is found that digital transformation improves the level of innovation across geographies by facilitating knowledge flow and information transparency6. The internationalization process of enterprises also imperceptibly affects the innovation performance of enterprises, and the strategic layout of enterprises’ internationalization is combined with enterprise innovation. Through the study of the sample of high-tech enterprises, it is found that the enterprise digital transformation can effectively promote the enterprise innovation. In the process of implementing the internationalization strategy, digital transformation still plays an important role in promoting the innovation of enterprises7.
In the context of the rapid development of digital technology, it is necessary to promote the deep integration of digital technology and the real economy. Empowering the real economy with digital technology is not only an important driving force for transforming the quality, efficiency and driving force of economic development, but also an important focus for achieving high-quality economic development. From the perspective of green technology innovation, this paper uses text analysis method to describe the degree of enterprise digital economy. Digital transformation promotes corporate green innovation by easing corporate financing constraints, weakening agency conflicts and stimulating corporate growth potential8. Enterprise innovation is a gradual process, and the dynamic capability theory constructs enterprise innovation into innovation ability, absorptive capacity and adaptive capacity9. By using multiple linear regression analysis method to analyze the data of A-share listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen, the analysis shows that there is A significant mediating effect between digital transformation and enterprise innovation performance. Among them, the mediating effect of absorptive capacity is the largest, while the mediating effect of adaptive capacity is the smallest, and there is no significant difference between state-owned enterprises and private enterprises with different property rights.
However, digitization also has its opposite. From the perspective of technology leap forward theory and strategic matching theory, Yu et al.10 adopted a questionnaire and found that enterprise digitalization has a non-linear impact on innovation performance. Organizational flexibility can positively regulate the double-edged sword effect of enterprise digitalization on innovation performance. Digital transformation only promotes the “increment” of enterprise technological innovation, but does not promote the “quality improvement” of enterprise technological innovation. This is caused by the “double arbitrage” and “herding effect” of enterprises. In order to obtain government subsidies or high arbitrage in the capital market, enterprises are keen to take advantage of digital transformation to increase the number of technological innovation. This will inhibit the “quality improvement” effect of technological innovation in digital transformation. The “herding effect” of technological innovation in the process of digital transformation makes enterprises’ technological innovation strategies converge, which will intensify the “incremental” effect of technological innovation in digital transformation and inhibit the “quality” effect of technological innovation in digital transformation11.
In summary, from the perspective of the relationship between digital transformation and innovation performance, most scholars believe that digital transformation will promote the improvement of innovation performance. The degree of digital transformation of enterprises is affected by the background of The Times, the nature of the industry, the proportion of property rights, regional differences and other multi-dimensional, so it is necessary to consider all the influencing factors in analyzing the relationship between digital transformation and innovation performance. The entry point of innovation performance in different industries should also be analyzed according to the characteristics of the industry.
ESG performance and innovation performance
In the context of corporate sustainable development, in order to maintain the relevant interests of stakeholders, good ESG performance will improve corporate innovation performance. An environment that serves the needs of stakeholders will elicit positive responses from stakeholders. Enterprises are more likely to obtain heterogeneous resources by actively improving their innovation capability, thus improving their innovation performance. Fulfilling social responsibility helps enterprises to obtain the support of stakeholders and necessary resources, thus promoting enterprise innovation performance. Good corporate governance will improve enterprise’s reputation and legitimacy, innovation benefit for the enterprise12. Based on the micro evidence of listed companies in China, it is found that ESG performance mainly reduces the cost of corporate debt financing by improving corporate information transparency, reducing corporate operational risks and alleviating corporate financing constraints, thus improving corporate financial performance and innovation performance13.
With the increasing requirements of government departments on corporate social responsibility, enterprises have to improve their own ESG performance to meet this trend. ESG performance has a more significant positive impact on enterprise innovation performance, especially in non-state-owned enterprises14. Compared with non-high-tech enterprises, high-tech enterprises’ ESG performance has a stronger promotion effect on enterprise innovation performance. It shows that enterprises can achieve significant innovation performance while improving the environment, actively fulfilling social responsibilities and strengthening corporate governance under the framework of sustainable development. In addition, the good ESG performance of enterprises can promote the improvement of innovation performance by improving the quality of internal control. This means that improving ESG performance plays a key role in strengthening internal governance, improving corporate transparency and reducing corporate risks.
In the context of the dual carbon strategy advocated by the state, enterprises with good ESG performance have stronger green technology innovation capabilities. Because the government will give more financing plans to these enterprises with good ESG performance, the cost of debt financing plays a partial intermediary role in this process15. Under different ownership nature, good ESG performance can promote the green technology innovation of both state-owned and private enterprises, and the promotion effect is stronger in state-owned enterprises. In different industries, the promotion effect of good ESG performance on GTI is stronger than that of heavy polluting enterprises in non-heavy polluting enterprises. As for the impact of regional differentiation, ESG performance has a significant role in promoting enterprise GTE in all regions, and compared with the central and western regions, ESG performance has a stronger role in promoting enterprise GTE in the eastern region. The horizontal comparison of enterprises can better highlight the impact of ESG performance on different enterprises. The unbalanced dynamic panel data of Chinese A-share listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen from 2012 to 2022 are used as the research sample, and the keyword frequency statistics are used to measure the degree of digital transformation. Based on the information asymmetry theory, resource-based theory and stakeholder theory, this paper analyzes the positive moderating effect of industry competition between digital transformation and enterprise ESG, and ESG performance has a positive impact on enterprise innovation16.
The multiple rating agencies and different rating methods of ESG have led to divergent ratings, bringing difficulties to users of ESG ratings and enterprises themselves. In the context of vigorously advocating innovation-driven green development, how ESG rating divergence affects the green behavior of micro enterprises is an important issue. By analyzing the sample of Chinese A-share listed companies from 2015 to 2021, this paper explores the impact and mechanism of ESG rating divergence on corporate green innovation17. The results show that ESG rating divergence promotes corporate green innovation. Mechanism analysis shows that this positive effect is realized through external pressure effect and internal driving effect. Further analysis shows that for enterprises with lower financial constraints, higher quality of internal control and older top management team, ESG rating divergence has a stronger effect on promoting green innovation.
In conclusion, ESG performance has a significant positive impact on the innovation performance of enterprises by improving corporate information transparency, reducing operational risks and alleviating financial constraints, and this impact varies among different enterprise types, industries and regions. At the same time, ESG rating divergence also plays a positive role in promoting corporate green innovation.
Impact of digital transformation and ESG performance on innovation performance
(1)
Digital transformation affects ESG performance and drives the growth of innovation performance.
The global attention to the disclosure of corporate ESG reports is increasing, and the company has incorporated the improvement of ESG performance into the scope of corporate strategy. Digital transformation affects the company’s ESG strategy. Digital transformation can promote the implementation of ESG strategy, help develop ESG assessment and monitoring technology, and improve enterprise information transparency; Thus, it can alleviate the financing constraints of enterprises and promote the improvement of financial performance and innovation level of enterprises. Digital transformation can positively moderate the relationship between ESG performance and enterprise innovation performance18.
Under the dual background of carbon peak and carbon neutral, digital transformation has a strong enabling effect on ESG responsibility fulfillment. It has a significant effect especially in state-owned enterprises and enterprises with low management shareholding ratio; It also points out that the government and regulatory authorities should constantly improve the incentive policies for enterprises’ digital transformation and relevant policies that are conducive to the improvement of enterprises’ ESG performance. It is convenient for enterprises to carry out digital transformation, improve the efficiency of enterprises, alleviate financing constraints, and promote the improvement of financial performance and innovation performance19.
Digital transformation is conducive to promoting enterprises to achieve sustainable development goals, improving ESG performance and enhancing long-term competitiveness20. Based on the text analysis and word frequency statistics of the annual reports of listed manufacturing companies, this paper constructs the variables of enterprise digital transformation, and studies the effect and mechanism of enterprise digital transformation on ESG performance. It is found that enterprise digital transformation has a significantly positive effect on ESG performance. Enterprise digital transformation can have a positive impact on ESG performance through improving enterprise green innovation performance, inhibiting managers’ myopic behavior and improving resource allocation efficiency. Moreover, analyst attention and media attention strengthen the promotion effect of enterprise digital transformation on ESG performance. In addition, enterprise digital transformation has heterogeneous impact on ESG performance. From the perspective of enterprise ownership nature, enterprise digital transformation has a positive impact on the ESG performance of state-owned enterprises and private enterprises. From the perspective of enterprise factor intensity, digital transformation has a significantly positive impact on the ESG performance of capital-intensive enterprises and technology-intensive enterprises. From the perspective of enterprise size hierarchy, digital transformation helps to promote the ESG performance of small and large enterprises.
(2)
ESG performance affects digital transformation, which in turn improves enterprise performance.
Digital transformation is a continuous process. This paper analyzes the data of Italian FTSEMIB listed companies as a research sample. Companies can quantify the choice of sustainable development goals into three indicators: environmental, social and economic. With the support of sustainable development theory, more attention should be paid to the impact of ESG performance on the company. Because good ESG performance can promote the digital transformation of enterprises, improve the financial performance, innovation performance and market value of enterprises21.
In recent years, with the increasing attention paid to the need for sustainable development, the company’s ESG performance has also attracted extensive attention from the government, the public and other related stakeholders; And has a non-negligible impact on the daily operation of enterprises. ESG can effectively improve the innovation output level of listed companies, and this promotion effect is more significant in large enterprises and state-owned enterprises. The construction of ESG affects the innovation level of listed companies mainly through three mechanisms: alleviating the financing constraints of listed companies, improving the innovation efficiency of employees and the risk-taking of enterprises. The reason is that ESG construction conveys the information of responsible social image to stakeholders. Promote trust, help enterprise digital transformation, dissolve the associated benefit the principal-agent conflict in the network, support for key resources of the enterprise innovation. ESG can not only promote the increase of innovation output of listed companies, but also effectively improve the quality of innovation. That is, ESG plays a dual role of “incrementally improving the quality” of innovation of listed companies. ESG uncertainty will weaken the promotion effect of ESG on innovation of listed companies22.
Corporate ESG responsibility performance plays a mediating role between digital transformation and innovation performance, and digital transformation has a significantly positive impact on innovation performance. The data of China’s listed companies from 2011 to 2021 were analyzed. This paper empirically tests the relationship between digital transformation and innovation performance, and further discusses the mechanism and influence path between the two. The data show that the impact of digital transformation on the innovation performance of enterprises in the eastern and central regions is stronger than that in the western and northeastern regions, and the impact on the innovation performance of large enterprises and technology-intensive enterprises is stronger than that of small and medium-sized enterprises, labor-intensive and capital-intensive enterprises. Based on this, we should dig into the advantages of enterprises’ digital transformation, build a new evaluation mechanism for ESG responsibility performance, and guide enterprises’ innovation and development by classification, so as to improve innovation performance23.
Under the background of double carbon, enterprise in order to whitewash the company report, enterprise floating green behavior appeared continuously. By analyzing the current situation of “greenwashing” in enterprise ESG reports, it is suggested that enterprises integrate ESG management strategy into the layout of enterprise digital transformation. Data-driven business process improvement can enable ESG to prevent “greenwashing”, improve enterprise innovation performance and promote sustainable development of enterprises24. Enterprises with green innovation capabilities are better able to apply emerging technologies such as blockchain, big data and cloud computing. Good ESG performance can promote the level of green technology innovation by strengthening internal supervision and improving information transparency of enterprises, and promote high-quality and efficient digital transformation of enterprises, thus promoting the improvement of financial performance and innovation performance of enterprises25.
To sum up, although the existing literature has achieved fruitful results on the independent or pairwise relationship among digital transformation, ESG performance and innovation performance, there are still significant theoretical blind spots in the synergy mechanism and dynamic evolution path among the three. First of all, the interaction between technology empowerment and institutional constraints has not been fully deconstructed, resulting in insufficient guidance for enterprise innovation on how to balance efficiency and responsibility; Secondly, the bidirectional causality and time-lag effect of DT and ESG have not been incorporated into a unified analysis framework, making it difficult to reveal the nonlinear relationship in complex situations. Finally, existing theories fail to integrate the joint shaping effects of technological resources and institutional resources on the dynamic capabilities of enterprises, which limits the strategic depth of management practice. Based on this, this study breaks through the traditional perspective of separation, constructs the ternary integration model of technology-institution-capability for the first time, and systematically explains how DT and ESG drive multi-dimensional innovation performance through complementary effect and balance effect. It also reveals the law of heterogeneity in different life cycle stages and policy environments. This framework not only deeps the interpretation boundary of resource-based view and dynamic capability theory in the digital era, but also provides an operational decision-making tool for enterprises to coordinate digital transformation and sustainable development.
Compared with the existing studies, the main contribution of this paper lies in innovatively proposing the inverted U-shaped nonlinear relationship between digital transformation and innovation performance. Breaking through the mainstream view of “digitalization promotes innovation linearly”, this paper reveals the mechanism that excessive digitalization may inhibit innovation due to resource imbalance from the perspective of technology transition theory. At the same time, the study found that ESG performance not only directly drives innovation, but also plays a mediating and regulating role between digital transformation and innovation. It verifies the synergistic effect of the two by improving the efficiency of environmental management and the transparency of governance, breaking through the limitation of the previous single action path. At the method level, the latest A-share data from 2017 to 2023 were used to cover the “dual-carbon” policy window period, the system GMM model was used to control the endogeneity, and the robustness of the conclusion was strengthened through variable substitution and heterogeneity test. Heterogeneity analysis further shows that the synergistic effect is generally established in different industries and firms with property rights, which revises the conclusion of traditional research that there are significant differences between regions or firm types. It provides a universal basis for policy coordination between digital transformation and ESG management.
Theoretical analysis and research hypotheses
Digital transformation and enterprise innovation performance
Digital transformation represents a holistic and strategic evolution of products, services, business processes, and organizational structures enabled by information technology, thereby fostering enterprise innovation. From the perspective of products and services, consumer demands for goods are becoming increasingly diversified. To meet these evolving needs, enterprises must transcend traditional knowledge frameworks, continuously enhance product quality, and expand service offerings. Digital transformation facilitates the integration and upgrading of existing technological systems and resource elements, enabling process reconfiguration and optimization, which in turn creates favorable conditions for fostering innovation. Furthermore, digital transformation can establish an integrated product platform that captures and analyzes user needs and experiences in real-time. Following product completion, feedback from users and market trends can be leveraged to drive transformation and upgrades, thereby enhancing innovation performance. From the standpoint of business processes, digital transformation dismantles market barriers, enabling swift and efficient integration of internal and external resources, shortening information flow cycles, and accelerating transformation processes. This empowers enterprises to more swiftly detect environmental changes, identify innovation opportunities, and bolster their competitive edge. Digital transformation can mitigate information asymmetry among various departments, enabling enterprises to identify critical financial information, effectively integrate the data, capital, and technology essential for innovation, reduce product development cycles, adopt flexible strategies to address unpredictable future demand fluctuations, and proactively expand the innovation ecosystem. From an organizational structure perspective, digital technologies and their applications are embedded into the internal processes of production, operations, and management within enterprises, thereby providing robust support for achieving intelligent production, reengineering sales processes, and fostering collaborative transformations in both management styles and business operation models. Digital transformation can redefine value creation mechanisms, assist enterprises in enhancing organizational efficiency, financial performance, and sustainable competitive advantages, ultimately driving innovation outcomes.
Technological transformation refers to the adoption of a novel technology in a specific domain that has not been previously utilized, with the aim of fostering development and economic growth. For less developed countries, some scholars argue that nations at the technological forefront cannot perpetually sustain their leadership position, as continuous emergence of subsequent imitators leads to a new techno-economic paradigm. Latecomers may leverage technological transitions to bypass the accumulation phase of human capital and fixed investment, thereby narrowing the productivity and output gap with technologically advanced countries. At the organizational level, digital technology transition is considered an emerging perspective that elucidates how enterprises in emerging markets can catch up with or even surpass mature enterprises by utilizing digital connectivity as a strategic tool. Given that digital technology facilitates the cultivation of enterprises’ creative, discovery, and exploratory capabilities, while enabling spatial breakthroughs, temporal leaps, and capability upgrades, its positive implications have been widely acknowledged by both academia and industry practitioners. However, the leapfrog development of digital technology still requires the leapfrog advancement of enterprise capabilities for support. The digitalization of the enterprise value chain facilitates the promotion of information and resource exchange within the value chain. By simplifying activities such as marketing and information exchange, it enables rapid feedback on user opinions and supports experimentation. As the digitalization of the enterprise value chain deepens, enterprise innovation performance is enhanced. Nevertheless, it is important to note that when all links in the value chain become excessively digitized, it may increase the complexity of the enterprise’s value creation process and incur higher operating costs, which could hinder the improvement of innovation performance and potentially suppress it. The digitalization of enterprise business processes allows for the recording of data from each link of the company’s internal business processes on a unified digital platform. Through the development of data analysis models and algorithms, integrated with business management scenarios, the performance of each business unit can be dynamically assessed and its future development trajectory predicted. As business process digitalization advances, enterprises can achieve cost reduction, operational efficiency enhancement, and foster innovation performance improvement. However, excessive digitization of business processes may result in misallocation of limited resources due to overinvestment, leading to excessive internal analysis that hinders real-time adjustments to enterprise innovation strategies. This imbalance can ultimately cause a decline rather than an increase in innovation performance. Product digitalization involves the research and development of intelligent digital products, which enable users to connect facilities and equipment seamlessly, capture user value requirements in real time, and accurately collect large-scale user data for strategic insights. Service digitalization can broaden the channels and scope for users to access services, enabling them to obtain more enterprise services at any time and in any place. Consequently, through the digital transformation of products and services, enterprises can unlock additional opportunities for value creation, thereby enhancing their innovation performance. However, over-reliance on digitalization may lead to substantial R&D investment requirements, causing a significant increase in product and service prices, which could negatively impact the sales performance of such innovative offerings. From the perspective of digital technology application, the initial extensive use of digital tools enhanced enterprise production technology levels, offering clear advantages in profit acquisition and performance improvement. Nevertheless, when the types and scope of digital technologies become overly expansive, the resource bases and capabilities of enterprises may fail to meet the demands of excessive digitalization, gradually weakening innovation performance. Excessive technological disparities and capability gaps can inhibit the positive effects of digitalization on innovation performance. Therefore, the implementation of enterprise digitalization does not necessarily result in improved innovation performance. Based on this analysis, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H1
There is an inverted U-shaped curve relationship between enterprise digitalization and innovation performance. In the early stage of digital transformation, the R&D dividend released by technology empowerment under resource constraint theory, the improvement of organizational agility under dynamic capability theory and the enhancement of knowledge diversity under complexity theory are discussed. When digital input exceeds the threshold of enterprise resource bearing (resource constraint), organizational adaptation (dynamic capability limitation) and technology integration (complexity critical point), resource misallocation, capacity-technology imbalance and system coordination cost surge will inhibit the improvement of innovation performance.
ESG performance and enterprise innovation performance
The ESG concept not only facilitates the achievement of the “dual carbon” goals but also enables enterprises to formulate practical plans for high-quality development. As the primary driver of high-quality economic growth, innovation serves as a critical tool for enterprises to achieve sustainability. By prioritizing ecological and environmental considerations, enterprises can gain the trust of stakeholders, enhance their reputation, reduce financing costs, and secure more high-quality resources. These efforts provide robust financial support and other accessible resources for enterprise innovation activities, thereby promoting improvements in innovation performance. The fulfillment of corporate social responsibility (CSR) permeates all aspects of business operations. It can alter external investors’ evaluations of enterprises in the short term while attracting top talent and increasing employee loyalty. Enhanced corporate governance ensures effective coordination between enterprises and stakeholders, enabling both internal and external supervision of management. This approach facilitates decision-making aligned with the company’s overall interests, reduces the likelihood of myopic managerial behavior, reinforces the understanding of the ESG concept and innovation for high-quality development, promotes the transformation of enterprise innovation outcomes, and ultimately enhances enterprise innovation performance.
Good ESG performance may exhibit a resource reallocation effect. Given the limited internal resources of enterprises, expenditures on environmental and social responsibility initiatives could potentially crowd out the financial resources required for operational activities and R&D investments. This can lead to insufficient operational inputs and R&D funding, thereby inhibiting the enhancement of a company’s R&D innovation capabilities. The managerial opportunism hypothesis suggests that corporate management’s motivation to engage in environmental protection and social responsibility is not primarily aimed at increasing shareholder value but rather at pursuing personal reputation and interests, such as obtaining political recognition. Furthermore, agency problems may result in enterprises allocating resources toward environmental protection and social responsibility fulfillment, which can have a crowding-out effect on core business operations.
On the one hand, existing studies have shown that corporate governance can significantly improve the internal control environment of enterprises, but to a certain extent, it will reduce the investment of enterprises in innovation projects with large capital needs, long R&D cycle and high risks. On the other hand, listed companies have some behaviors such as uneven quality of ESG information disclosure and “greenwashing”. The management may “greenwash” ESG reports in order to cover up the poor quality of financial status, trying to establish an environment-friendly and resource-saving corporate image26. However, this will aggravate information asymmetry and capital occupation, and inhibit the improvement of enterprise innovation performance.
To sum up, this paper proposes
H2
ESG performance has a positive impact on enterprise innovation performance.
Digital transformation, ESG performance and enterprise innovation performance
The key to improving enterprise ESG performance lies in addressing environmental, social, and governance issues as core priorities, ensuring continuous improvement, and enhancing overall performance to facilitate sustainable development. Supported by format upgrades and technological innovation, digital transformation plays a crucial role in advancing enterprise environmental management, corporate social responsibility, and governance levels, thereby effectively improving ESG performance. First, digital transformation can enhance the level of enterprise environmental management. By optimizing production and manufacturing processes through digitization and intelligence, as well as improving logistics and transportation capabilities, digital transformation reduces pollution and carbon emissions during product manufacturing, thereby elevating enterprise environmental management standards. Additionally, leveraging digital technology to overcome time and space limitations enables enterprises to establish smart and efficient ecological management information systems, further improving environmental management outcomes. Second, digital transformation can enhance the level of corporate social responsibility (CSR). On the one hand, as a novel tool for social governance, data analytics can significantly improve internal capabilities in data analysis, decision-making, and resource scheduling. This provides an effective approach to addressing complex social issues. Moreover, digital technologies possess characteristics such as zero marginal cost, economies of scale, and optimal resource allocation, which help mitigate information asymmetry among different governance entities, thereby elevating CSR standards. On the other hand, as digital transformation progresses to higher levels, enterprises can deeply integrate advanced digital technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence, and blockchain into their operations. This not only facilitates the construction of digital infrastructure but also promotes orderly social governance to meet the demands of multi-subject management, dynamic objects, and enhances both CSR levels and ESG performance sustainability. Third, digital transformation can elevate corporate governance standards. On the one hand, digital technologies enhance information transparency by enabling enterprises to efficiently collect, store, and analyze large volumes of data, thereby improving decision-making efficiency. Timely disclosure of key information and financial announcements reduces information asymmetry, thus enhancing corporate governance. On the other hand, digital transformation, as the integration of new information technologies with traditional economic models, creates development opportunities and breakthroughs for enterprises. It encourages them to transcend conventional thinking patterns, establish more flexible business strategies and management structures, and form a virtuous cycle within the corporate governance framework, ultimately promoting ESG performance improvement. Based on this, this paper proposes the following:
H3
Digital transformation can promote ESG performance and further affect enterprise innovation performance based on this.
The theoretical model of this paper is shown in Fig. 1.
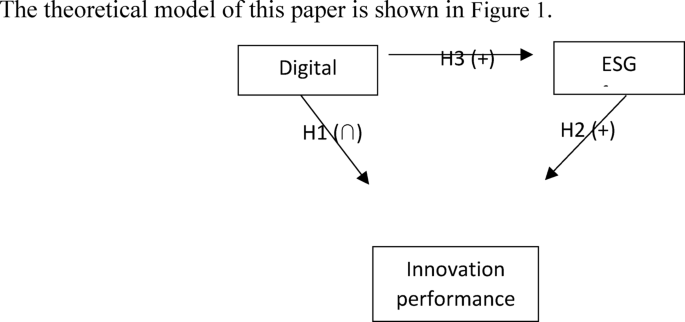
Figure 1 Theoretical model.
Research design
Sample selection
Selected 2004–2023 a-share listed companies in our country as the research object, and the following treatment: (1) to eliminate the financial sector, real estate company; (2) Eliminating ST and *ST companies; (3) eliminating the companies with missing observation data; (4) In order to avoid the abnormal influence of outliers on the model estimation, all continuous variables are winsorized, and the winsorized objects are the upper and lower 1% of the observed values. After the above elimination, Stata17 was used for data processing and analysis. Finally, 29,135 pieces of valid data were selected. The sample data used were taken from China Stock Market & Accounting Research Database (CSMAR) and Chinese Research Data Services platform (CNRDS).
The model design
Based on the above theoretical analysis and the research hypothesis, constructs the benchmark model and adjusting effect inspection, specific model is as follows:
In order to verify whether enterprise digital transformation can promote the improvement of enterprise innovation performance, a benchmark regression model is established:
$${\text{EIP}}_{{i,t}} = \alpha _{0} + \alpha _{1} {\text{EDT}}_{{i,t}} + \alpha _{2} {\text{EIP}}_{{i,t}} ,t – 1 + \alpha _{3} {\text{Control}}_{{i,t}} + \Sigma {\text{Enterprise}} + \Sigma {\text{Year}} + \varepsilon _{{i,t}}$$
(1)
$${\text{EIP}}_{{i,t}} = \beta _{0} + \beta _{1} {\text{ESG}}_{{i,t}} + \beta _{2} {\text{EIP}}_{{i,t}} ,t – 1 + \beta _{3} {\text{Control}}_{{i,t}} + \Sigma {\text{Enterprise}} + \Sigma {\text{Year}} + \varepsilon _{{i,t}}$$
(2)
$${\text{EIP}}_{{{\text{i}},{\text{t}}}} = \gamma _{0} + \gamma _{{\text{1}}} {\text{EDT}}_{{{\text{i}},{\text{t}}}} + \gamma _{{\text{2}}} {\text{ESG}}_{{{\text{i}},{\text{t}}}} + \gamma _{{\text{3}}} {\text{EIP}}_{{{\text{i}},{\text{t}}}} ,{\text{t}} – {\text{1}} + \gamma _{{\text{4}}} {\text{Control}}_{{{\text{i}},{\text{t}}}} + \Sigma {\text{Year}} + \Sigma {\text{Industry }} + \varepsilon _{{{\text{i}},{\text{t}}}}$$
(3)
In the above formula, the subscripts i and t represent the enterprise and the year in turn; EIP represents innovation performance; EDT stands for enterprise digital transformation; ESG refers to corporate ESG responsibility; Model (1) is mainly used to test the total effect of digital transformation on innovation performance, and the coefficient α1 is the impact degree of digital transformation on enterprise innovation performance. The coefficient β1 in Model (2) represents the impact of ESG performance on enterprise innovation performance. The coefficient γ1 in Model (3) represents the direct effect of digital transformation on innovation performance; Coefficient γ2 is the moderating effect of enterprise ESG performance, that is, the effect of digital transformation on improving innovation performance by strengthening enterprise ESG responsibility performance. Furthermore, the fixed effects of Enterprise and Industry have been incorporated into the empirical model.
Variable definitions
Explained variable: Enterprise Innovation Performance. In the existing literature, the way of measuring the performance of enterprise innovation mainly has two kinds: one is based on the patent, the total enterprise patent license or patent cited times as the measurement indicators; Second, the sales volume of new products is used as the indicator to measure innovation performance. Since China does not require enterprises to disclose the sales revenue of new products in the annual report, based on the availability of data, this paper uses the natural logarithm of the total number of patents granted plus 1 to measure the innovation performance of enterprises.
Explanatory variable: Digital Transformation. Considering that it is impossible to judge the degree of digital transformation achieved by enterprises by extracting keywords from the annual report alone, this paper draws on the approach of Zhang et al. (2021) to measure digital transformation using the portion of the notes to the financial reports of listed companies that are related to digital transformation in the intangible assets line item (“computer software” “grid access system” “computer software “, “ERP systems”, “intelligent platforms”, etc.) to total intangible assets to measure digital transformation27.
Control variables: Referring to previous studies28,29,30,31,32 and considering the key factors affecting the ESG performance of enterprises, the following control variables are selected: Company Size (Take the logarithm of total assets), Company listing age (The number of years the enterprise has been listed), Company Growth (Growth rate of operating income), and asset-liability ratio (Total liabilities/total assets of the company at the end of the year), Proportion of independent directors (Number of independent directors/Total number of directors), Proportion of equity concentration (The shareholding ratio of the largest shareholder), Board size (Take the logarithm of the number of board members).
Moderating variable: ESG Performance. The ESG rating assigned by Sino-Securities Index is used to measure the ESG performance of enterprises. The rating assigned by Sino-Securities Index is divided into nine grades from C to AAA according to the indicators. In this paper, the nine grades are assigned 1 to 9 respectively to obtain variable ESG.
Descriptive statistics
For the study of enterprise digitalization, ESG and innovation performance, the relationship between the first from the artificial intelligence technology, cloud computing, big data, block chain technology and digital technology using five aspects conclude a digital key word; Secondly, Python was used to search and match the feature words and make word frequency statistics. Sum of each enterprise is discussed, the key word frequency to measure the degree of enterprise digital transformation, in order to eliminate the right data, on the basis of the original plus 1 take natural logarithm, to measure the digital transformation. The annual average score of ESG is used to measure the ESG performance of the enterprise. The natural logarithm of the total number of patents granted plus 1 is used to measure the innovation performance of the enterprise.
Firstly, descriptive statistics were used to analyze the digital transformation, ESG score and innovation performance. The results are shown in the following Table 1.